- Pulse 110 After Eating
- Pulse Rate Over 100 Indicates What
- Pulse 110 Bpm
- Pulse 110 When Walking
- Pulse 110 Resting
- Pulse 110-116 Means What
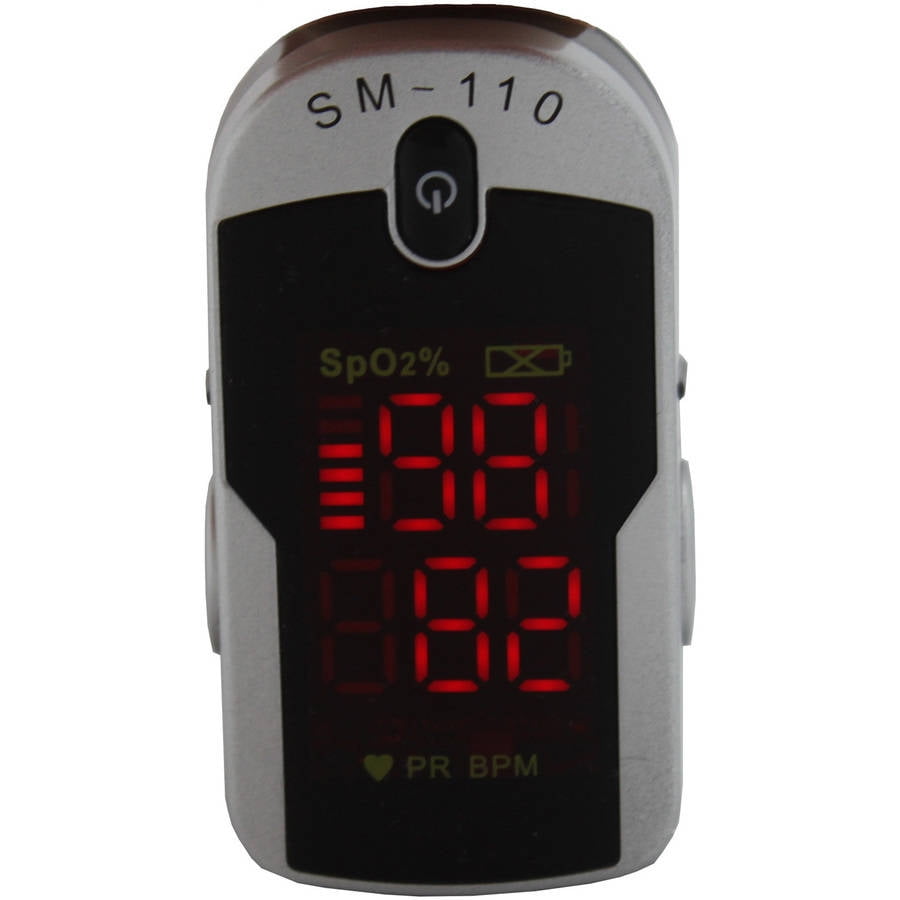

Elevated Heart Rate Most Likely Caused by Medical Condition

May 6, 2011
Dear Mayo Clinic:
The target heart rate is a guideline which can help you stay in a safe exercise heart rate range. This will help you improve your cardiorespiratory fitness. This means your heart and lungs will become stronger. As your age increases, your target heart rate will decrease. Learn how to measure your pulse /. The cause of low blood pressure with a high pulse varies. Sometimes, symptoms occur after a specific activity, such as standing up too quickly, while others result from an underlying issue. Tachycardia refers to a heart rate that’s too fast. How that’s defined may depend on your age and physical condition. Generally speaking, for adults, a heart rate of more than 100 beats per minute (BPM) is considered too fast. View an animation of tachycardia. A pulse of 110 means that your heart is beating 110 times per minute. In a healthy adult who is resting — a rate of 110/min is considered tachycardia (higher than normal value) In an exercising adult, that rate is normal. However in diseased condition, a pulse of 110/min by itself does not mean much.
What is sinus tachycardia? What causes it? How is it treated?
Pulse 110 After Eating
Answer:
Sinus tachycardia is the term used to describe a faster-than-normal heartbeat — a rate of more than 100 beats per minute versus the typical normal of 60 to 70 beats per minute. Well over 99 percent of the time, sinus tachycardia is perfectly normal. The increased heart rate doesn't harm the heart and doesn't require medical treatment.
The term sinus tachycardia has nothing to do with sinuses around the nose and cheeks. Rather, it comes from the sinus node, a thumbnail-sized structure in the upper right chamber of the heart. This structure controls the heart rate and is called the heart's natural pacemaker.


Pulse Rate Over 100 Indicates What
The sinus node signals the heart to speed up during exercise or in situations that are stressful, frightening or exciting. For example, a 10- to 15-minute brisk walk typically elevates the heart rate to 110 to 120 beats per minute. Also, the sinus node increases the heart rate when the body is stressed because of illness. In all of these circumstances, the heart rate increase is a normal response.
Likewise, the sinus node signals the heart to slow down during rest or relaxation.
We see patients who are concerned because their heart rate stays elevated in the range of 100 to 130 beats per minute. Almost always, there is a medical reason that the sinus node keeps signaling for the faster rate. Possibilities include anemia, an underlying infection, elevated thyroid hormone, or reaction to medication. Addressing those conditions would likely bring the heart rate back to a normal rate. Other factors may be involved, too, such as overdoing caffeine. For example, I saw one patient who was eating several chocolate bars a day. The caffeine in the chocolate was elevating her heart rate.
Rarely, the sinus node can jump-start the heart rate with no apparent cause — no stress, illness or high activity level. This is termed inappropriate sinus tachycardia. About half of the time, this phenomenon occurs after recovery from a serious illness, usually a viral illness. And most often, those affected are women in their 20s and 30s.
Inappropriate sinus tachycardia doesn't cause heart damage, though patients may feel uncomfortable with the elevated heart rate. Some patients may have other associated symptoms such as fatigue, headache, chest discomfort, shortness of breath or light-headedness. When symptoms are problematic, treatment can include beta blockers that block the action of adrenaline and help slow the heart rate. Very rarely, the heart may maintain very high rates of 160 to 180 beats per minute. More involved treatment options are available to control this condition.
For some patients, the elevated heart rate is the only symptom. Some have a lifelong history of sinus tachycardia in the 110 beats per minute range, and they lead a normal, healthy life. And often the inappropriate sinus tachycardia will improve in time without treatment.
We encourage patients with prolonged sinus tachycardia to improve their overall fitness level. The more fit you are, the lower your resting heart rate. The elevated heart rate could slow with improved conditioning.
Patients who have concerns about an elevated heart rate should check with their physician. Other conditions, such as atrial fibrillation, can cause a racing heart. Atrial fibrillation should be treated, as it increases the risk of stroke and can damage the heart.
— Stephen Hammill, M.D., Cardiology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn.
To determine if 110 is a good or a bad resting pulse rate please select if you are analyzing the heart rate of a child (0-10 years) or a young adult / adult (10-99) years:
The heart rate was measured on a
Pulse 110 Bpm
There are a lot of factors that influence the human heart rate, such as the physical fitness, medications, emotional changes or simply the air temperature and the position of the body.
Pulse 110 When Walking
But most of all, the heart rate changes on the person growing up and becoming older. While a pulse of 150 on a 3 month old child can be perfectly within normal range it would be quite worrying to have said pulse as an adult.
Pulse 110 Resting
Why is that?
Elephant and mouse - completely different heartbeats
Typically, small mammals have a much faster heart rate than larger mammals. For example, the resting heart rate of an adult mouse is about 500 bpm while elephants have a resting heart rate of around 28 bpm.Larger animals obviously do have larger hearts too, and they again are connected to larger veins and larger arteries.Therefore their hearts can generate great pressures while pumping blood, and due to the quantity it also takes longer for the pressure to push the blood to limbs 'far' away.
Pulse 110-116 Means What
