R programming Codes Cheat Sheet by deleted - Cheatography.com Created Date: 1548Z. The examples use the traditional built-in R data sets (such as the iris data, used to create the neural network above), so there's unfortunately not much of a “big data” aspect to the reference card. But if you're just getting started with prediction and classification models in R, this cheat sheet is a useful guide.
How to use chmod codes in UNIX:
- There are three types of permissions in files and folders in unix
- Read (r)
- Write (w)
- Execute (x)
- And, there is a classification of users called UGO (explained bellow):
- U ~> User (usually, you)
- G ~> Group (eg sudo group)
- O ~> Others
When you run $ ls -l your output will be something like this:
How to read this?
Where is a letter put a 1 and where is a - put a 0. Examples:
| U | G | O |
|---|---|---|
| r w x | r w x | r w x |
| 1 1 1 | 1 1 1 | 1 1 1 |
So, user, group and others can read, write and excute the file or folder
| U | G | O |
|---|---|---|
| r w - | r -- | r - x |
| 1 1 0 | 1 0 0 | 1 0 1 |
So, user can read and write, group can only read, finally other can read and execute
As you can see, we can play with these permissions
| U | G | O |
|---|---|---|
| r - x | r w - | - - - |
| 1 0 1 | 1 1 0 | 0 0 0 |
| U | G | O |
| - w x | r - x | - - x |
| 0 1 1 | 1 0 1 | 0 0 1 |
Finally, the codes! (sorry)
| Bin | Decimal | Representation |
|---|---|---|
| 000 | 0 | - - - |
| 001 | 1 | - - x |
| 010 | 2 | - w - |
| 011 | 3 | - w x |
| 100 | 4 | r - - |
| 101 | 5 | r - x |
| 110 | 6 | r w - |
| 111 | 7 | r w x |
The syntax is something like this: $ chmod u/permissions g/permissions o/permissions file[or /dir/]
- So, if I run
$ chmod 777 file<=>rwx rwx rwxeverybody can do anything with file - Or I run
$ chmod 744 dir<=>rwx r-- r--only user can read, write and execute, group and others only read dir. - Or run
$ chmod 200 file2<=>-w- --- ---only you can write file2
Thanks for reading, I hope it works! Follow me on Twita and GitHub
Refs:
Special thanks:
- Gabe Kutuzov (GitHub)
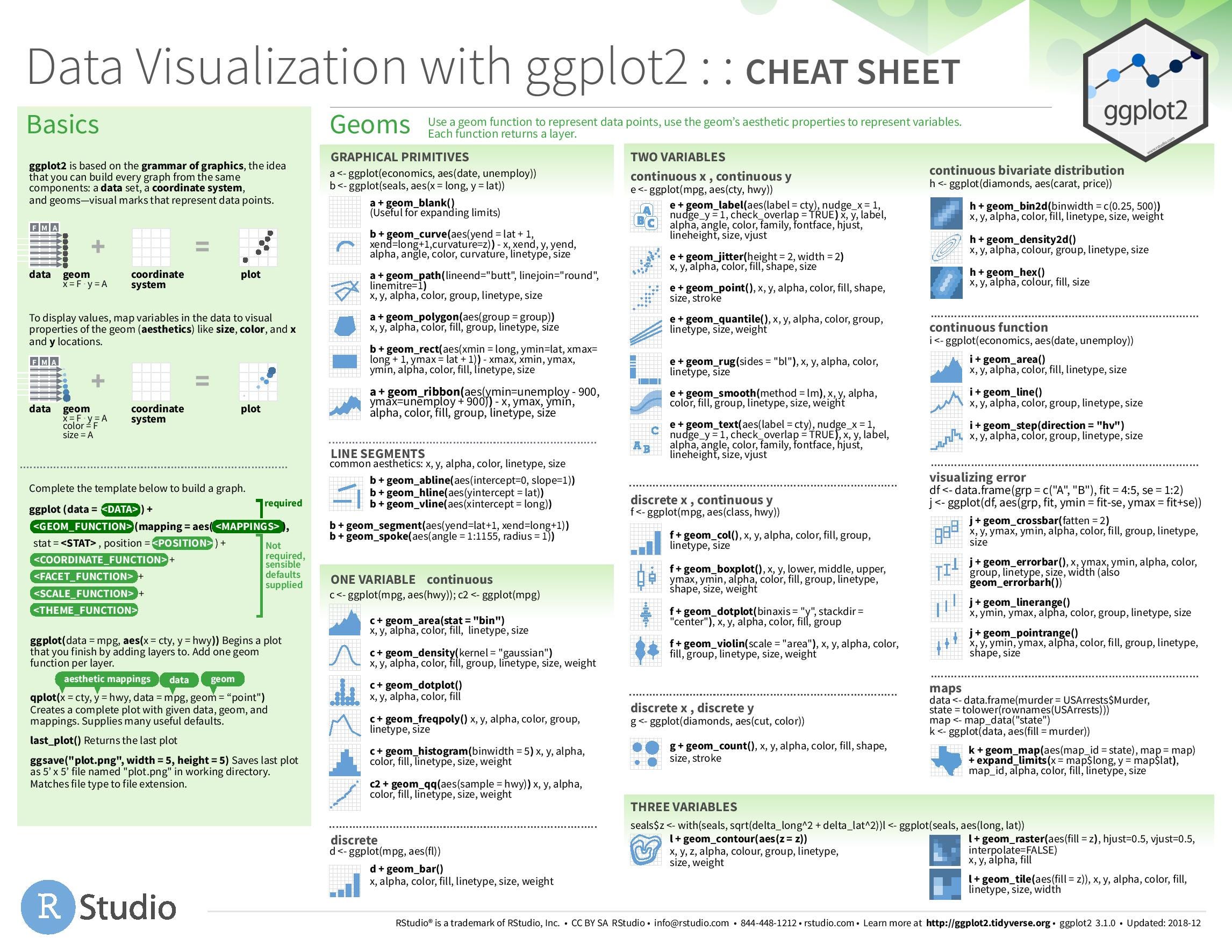
I reproduce some of the plots from Rstudio’s ggplot2 cheat sheet using Base R graphics. I didn’t try to pretty up these plots, but you should.
I use this dataset
The main functions that I generally use for plotting are
- Plotting Functions
plot: Makes scatterplots, line plots, among other plots.lines: Adds lines to an already-made plot.par: Change plotting options.hist: Makes a histogram.boxplot: Makes a boxplot.text: Adds text to an already-made plot.legend: Adds a legend to an already-made plot.mosaicplot: Makes a mosaic plot.barplot: Makes a bar plot.jitter: Adds a small value to data (so points don’t overlap on a plot).rug: Adds a rugplot to an already-made plot.polygon: Adds a shape to an already-made plot.points: Adds a scatterplot to an already-made plot.mtext: Adds text on the edges of an already-made plot.
- Sometimes needed to transform data (or make new data) to make appropriate plots:
table: Builds frequency and two-way tables.density: Calculates the density.loess: Calculates a smooth line.predict: Predicts new values based on a model.
All of the plotting functions have arguments that control the way the plot looks. You should read about these arguments. In particular, read carefully the help page ?plot.default. Useful ones are:
main: This controls the title.xlab,ylab: These control the x and y axis labels.col: This will control the color of the lines/points/areas.cex: This will control the size of points.pch: The type of point (circle, dot, triangle, etc…)lwd: Line width.lty: Line type (solid, dashed, dotted, etc…).
Discrete
R Code Cheat Sheet
Barplot
Different type of bar plot
Continuous X, Continuous Y
Scatterplot
Basic R Syntax Cheat Sheet
Jitter points to account for overlaying points.
Add a rug plot
Add a Loess Smoother
Loess smoother with upper and lower 95% confidence bands
Loess smoother with upper and lower 95% confidence bands and that fancy shading from ggplot2.
Add text to a plot
Discrete X, Discrete Y
Mosaic Plot
Color code a scatterplot by a categorical variable and add a legend.
par sets the graphics options, where mfrow is the parameter controling the facets.
The first line sets the new options and saves the old options in the list old_options. The last line reinstates the old options.
This R Markdown site was created with workflowr
